The Disadvantages and Advantages of Using Bitcoin and Blockchaine
This research report is about the most popular digital currency in the world, Bitcoin, and how it relates to crime. Part of this report details how Bitcoin works in detail. Both user and behind the scenes perspectives will be analyzed. An explanation of how Bitcoin denominations, the different types of Bitcoin wallets, and where to buy Bitcoin is examined. The ethical issues that have to do with using Bitcoin instead of traditional currency, how Bitcoin relates to criminal activities, and the future of Bitcoin are all covered in this report. The advantages and disadvantages of Bitcoin are explained. Towards the end of this report, my views as a Bitcoin user are shared, as well as where Bitcoin is going in the future. Bitcoin and its ethical implications on society require extensive research, collaboration, and unity in order to provide a truly digital currency.
Bitcoin is defined by Oxford Dictionary as “a type of digital currency in which encryption techniques are used to regulate the generation of units of currency and verify the transfer of funds, operating independently of a central bank”. Although this definition implies that Bitcoin is simply just a digital currency, the definition from Bitcoin.org describes Bitcoin as “a consensus network that enables a new payment system and a completely digital money. It is the first decentralized peer-to-peer payment network that is powered by its users with no central authority or middlemen. From a user perspective, Bitcoin is pretty much like cash for the Internet.” This is a very important distinction because Bitcoin is actually more than just a digital currency, it’s an entirely new technology that uses peer-to-peer and no central authority to create a payment system unlike any ever before. To understand this system, we start by reviewing the technology that drives Bitcoin and its network.
Bitcoin can be sent and received through Bitcoin wallets, which are similar to bank accounts. Anybody with access to the internet can create as many Bitcoin wallets as they want. A user can send or receive Bitcoin using their Bitcoin wallet. When they do this, they create a transaction, which is recorded on the Bitcoin network’s block chain. The block chain acts as a public ledger, where anybody can see transactions that are occurring on the network. However, the sender and receiver of the Bitcoin remain transparent. The Bitcoin network uses the block chain to verify that everyone’s balance is correct. If a node in the Bitcoin network does not possess the same information as everyone else, than the Bitcoin network will know that is not a correct balance. In fact, every single Bitcoin transaction can be traced back to the origin of the first Bitcoin transaction.
There are a few different types of Bitcoin wallets which can be used to store your Bitcoin. The most common type of wallet is a software wallet. This wallet is basically the same as a computer program or application you install. Once installed, you have access to your private key, so only you are able to view and use your wallet. Software wallets are sort of the middle ground between convenience and security. Web wallets are more about convenience. Although they are less secure, your wallet will be synced across all of your devices. This means you can send and receive Bitcoins from your mobile phone, and have an updated balance when you check your computer later. The security issues of web wallets are mostly due to the fact that you have to put trust in the web wallet provider. They must have enough security measures to prevent anything bad happening to your wallet. The best way to use web wallets is to use them while you need them, but if you have funds just sitting around, it is best to transfer them to a different wallet that is not a web wallet. Finally, the most secure wallet type is a paper wallet. Paper wallets are actually really different in the sense that you can write down your public and private keys on a piece of paper, and still be able to receive Bitcoins. In order to access your funds, you have to import your private key into a different Bitcoin wallet. However, even when your wallet isn’t connected to the internet, users can still send you Bitcoin using your public key. You won’t actually be able to use them until you import your paper wallet to a computer and sync up with the Bitcoin network, but in practice you can still receive funds while your wallet is offline. This makes them the most secure wallet available.
The price of Bitcoin has grown too large to make sending whole Bitcoins practical for everyday use. For example, sending $20 worth of Bitcoin means sending just a fraction of what a whole Bitcoin is actually worth. It is for this reason that every Bitcoin is able to be broken down into smaller parts. Fractions of a Bitcoin can be sent down to the hundredth of a millionth of a Bitcoin. This is the smallest unit of Bitcoin and it is called a Satoshi, named after the creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto. Table 1 below shows how Satoshi are worth practically nothing by themselves. In fact, many games and apps give away free Satoshi just for playing while ads run in the background. In is interesting to note how big of a difference the price of Bitcoin has on these denominations. If you take a look at milliBitcoin in Table 1, you can see that at a value of $100 per Bitcoin, it is only worth $0.10. However, when Bitcoin is worth $500, the value increases to $0.50. This shows how Bitcoin prices can change dramatically, and even small amounts of Bitcoin can very quickly gain or lose value.
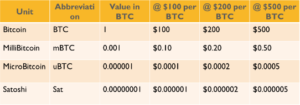
Table 1: This table shows the various denominations of Bitcoin and their value and different prices.
Purchasing Bitcoin is actually pretty simple. There are numerous online exchanges on the Internet that exchange traditional currencies and Bitcoin. These exchanges sell and buy Bitcoin at the going rate for Bitcoin, which is determined mainly by current events and demand for Bitcoin. The exchanges often take a fee for providing you with the service of exchanging Bitcoin and currency. However, if you want to purchase Bitcoin in person, there is no exchange fee. There are some websites that match buyers and sellers of Bitcoin to meet up in person. Buying Bitcoin in person is more anonymous because you don’t have to give your personal information out to purchase the Bitcoin. All that is required is that you meet up, exchange Bitcoin and cash, and the transaction is complete. There are no logs detailing your name, address, credit card number, or other identifying information. With that in mind, it is probably a good idea to meet in a public place, preferably with cameras to ensure that you are not robbed or mugged during your exchange of digital and traditional currency.
Bitcoin, like most currencies, can be used for illegal activities. The most well-known place to use Bitcoin for illegal purchases is the Silk Road. At this “dark market” website, it is possible to purchase a number of illegal things such as drugs, passports or identities, hacking services, and much more. Silk Road has been shut down, but there are multiple sites that are ready to replace it. Looking at Table 2, there were a total of 41,207 illegal listings on these “dark market” websites in 2014 (Caffyn). In addition to the other illegal content being sold, weapons were also included in some of these websites. Bitcoin is being used for these illegal purposes because of its anonymity. Using Bitcoin, people are able to purchase these illegal items or services and remain anonymous to the general public and the authorities. Although other currencies also fund criminal activities, Bitcoin may be the first widely used currency that is hard enough to trace that allows for illegal purchases to be made anonymously over the web. That being said, Silk Road was shut down, so even though Bitcoin was used, it is not impossible to catch these criminals.
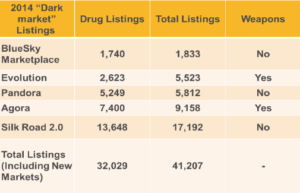
Table 2: This table shows the number of drug and total listings for known “dark market” websites during 2014. The right most column also explains whether or not the website sold weapons in addition to drugs.
Now that we have looked into how Bitcoin is used for illegal activities, it is possible to examine the advantages and disadvantages of using Bitcoin. One of the best things to come out of Bitcoin is the fact that counterfeiting Bitcoin is literally impossible. Since all of the Bitcoin network knows all Bitcoin addresses’ balance, anything that is in error of that will automatically be rejected by the network. In addition, the Bitcoin block chain can detect whether a Bitcoin has already been “spent” or not. This is to prevent people from trying to use the same Bitcoin for multiple transactions. Another advantage of Bitcoin is the reduced risk for identify theft. When you use Bitcoin, all you have to do is give out a receiving address or send Bitcoin to someone else’s address. You don’t have to give out your personal information, like your name, phone number, address, social security number, credit card information, or anything else. Bitcoin can be used with just two wallet addresses. A third important advantage is that Bitcoin can be exchanges at extremely high rates. A Bitcoin transaction is usually detected within a matter of seconds, but it can take anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour before the funds are usable. This is to ensure that the transaction has enough confirmations by the network to mark it as a valid transaction. If enough nodes agree with the transaction, the funds are available for use. Another advantage of Bitcoin is that you can reach historically inaccessible markets. Anyone with an internet connection can obtain and send Bitcoin. This means over 3 billion people in the world can buy your product if you are accepting Bitcoin as a payment. The final advantage of Bitcoin is the low cost of fees. Although exchange fees can sometimes be high, sending Bitcoin to and from another Bitcoin address is extremely cheap. Often is in the range of a few cents or less to send a transaction.
There are fewer disadvantages of Bitcoin than advantages, but they are all significant enough to warrant discussion. Obviously the number one disadvantage of Bitcoin is the fact that it can be used to finance illegal or immoral activities. Criminals that use Bitcoin to purchase illegal drugs, weapons, identities, passports, or other items is one of the downsides of Bitcoin. Another disadvantage is the high risk of loss. Bitcoin should be considered a high risk asset. The price fluctuations can often change how much a Bitcoin is worth in a matter of hours, sometimes even shorter than that. The high risk of loss is mostly due to its excessive price volatility. Depending on current events, the economy, and other numerous factors, Bitcoin could either see big gains or big losses at very quick intervals. A final disadvantage worth mentioning is the fact that lost Bitcoin is unrecoverable. If you misplace or lose your Bitcoin wallet, it is essentially impossible to get your funds back. If your wallet is stolen or lost, there is no place that will reimburse you or even help you track down who stole your Bitcoin. Basically, once your Bitcoin is spent, it is gone for good.
One of the major ethical theories that is relatable to Bitcoin and crime is the social contract theory. The social contract theory states that “Morality consists in the set of rules, governing how people are to treat one another, that rational people will agree to accept, for their mutual benefit, on the condition that others follow those rules as well” (Quinn 82). Since we as a society used currency to exchange goods and services, and Bitcoin is a type of currency, Bitcoin should be under the same social contract we sign when we use traditional currency. In this aspect, traditional currency is also used for illegal activities and crime. As long as everyone uses Bitcoin in a legal and safe way, it is ethical, or at least no less ethical than traditional currency is.
The other ethical theory that Bitcoin relates to is Act Utilitarianism, which has a principle of utility. This principle states “An action is right (or wrong) to the extent that it increases (or decreases) the total happiness of the affected parties” (Quinn 73). Now, it might be confusing to suggest money is happiness, but for the sake of this argument let’s look at some number data. In 2014, the daily sales volume for all the dark markets was approximately $650,000 (Caffyn). This seems like a large amount at first glance. However, that number is relatively low in comparison to all of the Bitcoin transactions. According to bitcoincharts.com, there were 2.9 million Bitcoin, worth approximately $1,143,586,000, sent on December 8, 2015. This number greatly exceeds the $650,000 of illegal daily dark market transactions, so it is likely that the number of legal transactions far exceeds the number of illegal ones. However, it is important to note that is impossible to tell how much of that Bitcoin was used for legal or illegal purposes. There is no data on what or where this Bitcoin is spent on. Still, the number of total Bitcoin sent is so large that when compared with the data for daily dark market transactions in 2014, it seems likely that Bitcoin is ethical in the sense that more people are using it for legal means than illegal means.
As a Bitcoin user, I can’t help but want to see Bitcoin succeed. It’s not so much that I want all money to become digital, it’s more the benefits that Bitcoin can bring to our society. If you could have the same security you do now with credit cards, but have transactions be processed much faster, know that counterfeit money was impossible, and share less personal information with buyers and sellers, wouldn’t you feel more comfortable with buying things online? Regardless, Bitcoin is still a very young currency. It was introduced in 2009, much younger than our familiar paper dollar bill, which was released in 1861. I also think that storing large amounts of money in Bitcoin is NOT a good idea. If you are sending a few hundred dollars to someone, you might be out a few cents or at most a dollar due to price fluctuations of Bitcoin. However, if you are sending upwards of a hundred thousand dollars, you could potentially be losing hundreds if not thousands of dollars because of a price fluctuation. That being said, I think it’s really cool that services like PayPal accept Bitcoin to fund your account. Since you are able to fund your PayPal account with Bitcoin, you can buy almost anything on the Internet using Bitcoin.
The future of Bitcoin is an interesting one. Many people are concerned that, due to Bitcoin’s design, there will only ever be 21 million Bitcoin in existence. These people fail to realize however, that each Bitcoin is divisible by up to 10^8. This allows for extreme scalability and inflation for the future. Bitcoin’s future could also be deterred by “alt coins.” Alt coins are basically Bitcoin copy cats – they use similar technologies but try to improve on something that Bitcoin might be poor at doing. Most have small user bases, but one of them could take off in an instant and Bitcoin would become obsolete. However, I think if Bitcoin does not survive, the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies will. There is no possible way to stop the innovation of the block chain technology, and I think parts of it could be incorporated into services like paychecks, Government services, voting, and business to business transactions. Overall though, since Bitcoin is still so young, the future of Bitcoin is unknown.
Bitcoin is a digital currency that can redefine how we pay for things. It uses a system that can help us improve our online payments by improving our security, reducing identity theft, eliminating counterfeit money, and speeding up transactions. The ethical implications of Bitcoin are mostly goods ones. However, with every great innovation comes bad people trying to do bad things. Illegal websites and terrorist groups using Bitcoin to finance themselves will have to be pursued just like criminals who use traditional currency. The world might not be ready for a completely digital currency, but it doesn’t mean we shouldn’t try to develop one. That way, when the world is ready, Bitcoin will be ready.
MLA Works Cited
- Caffyn, Grace. “Bitcoin on the Dark Web: The Facts.” CoinDesk RSS. N.p., 23 Sept. 2015. Web. 10 Dec. 2015. <http://www.coindesk.com/bitcoin-on-the-dark-web-the-facts/>.
- DeMartino, Ian. “The Many Types and Functions of Bitcoin Wallets.” Coin Telegraph. N.p., 20 June 2014. Web. 10 Dec. 2015. <http://cointelegraph.com/news/111891/the-many- types-and-functions-of-bitcoin-wallets>.
- Kenigsberg, Marc. “Bitcoin Units and Denominations – Explained Simply | Bitcoin Chaser.” Bitcoin Chaser. N.p., 26 Oct. 2013. Web. 10 Dec. 2015.
- <http://bitcoinchaser.com/bitcoin-units-and-denominations>.
- Quinn, Michael J. “Social Contract Theory.” Ethics for the Information Age. Boston:
- Pearson/Addison-Wesley, 2005. 82. Print.
- Zohar, Aviv. “Bitcoin: Under The Hood.” Communications Of The ACM 58.9 (2015): 104-
- 113. Academic Search Premier. Web. 9 Dec. 2015.
Cite this page
The Disadvantages and Advantages of Using Bitcoin and Blockchaine. (2022, Dec 04).
Retrieved May 30, 2025 , from
https://supremestudy.com/the-disadvantages-and-advantages-of-using-bitcoin-and-blockchaine/
Having doubts about how to write your paper correctly?
Our editors will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Get started
Leave your email and we will send a sample to you.
Thank you!
Please check your inbox